
Select Links
- Winter Webinar Series Flyer 2020-2021
- 5th Annual Local Government Innovation Conference
- Local Government Charitable Contributions
- Recorded Webinars
- SFY 2017-2018 Annual Report: Administration of Local Government Efficiency Program
- County-wide Shared Services
- Senior Housing Regulations Two Model Laws
- Local Laws Search
- Local Government Handbook
- Local Government Technical Assistance
- LGe Knowledge Matrix
- LGt On-Site Course Listing
- LGt Online Interactive Courses
- LGt Online Videos
- Resources for Local Governments
- Contact Local Government Services
- Municipal Restructuring Fund
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a regional economic development agency that represents a partnership of federal, state, and local government established by the Federal Appalachian Regional Development Act of 1965. Its goal is to improve the economy and quality of life in Appalachia by providing funding and technical assistance for projects in areas such as business development, education and job training, telecommunications, infrastructure, community development, housing, and transportation. These projects create thousands of new jobs; improve local water and sewer systems; increase school readiness; expand access to health care; assist local communities with strategic planning; and provide technical and managerial assistance to emerging businesses.
Appalachia
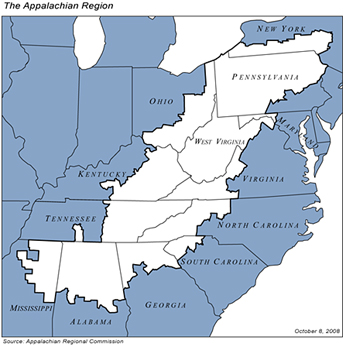 New York State is one of the thirteen states in the federally-defined Appalachian region that includes all of West Virginia, and parts of Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, Virginia, Kentucky, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia, Alabama and Mississippi.
New York State is one of the thirteen states in the federally-defined Appalachian region that includes all of West Virginia, and parts of Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, Virginia, Kentucky, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia, Alabama and Mississippi.
Under the program, the States are responsible for recommending projects for Federal ARC assistance. The following five investment goals are identified in ARC’s Strategic Plan, “Investing in Appalachia’s Future: The Appalachian Regional Commission’s Five-Year Strategic Plan for Capitalizing on Appalachia’s Opportunities 2016-2020”.
- Goal 1: Economic Opportunities
Invest in entrepreneurial and business development strategies that strengthen Appalachia’s economy. - Goal 2: Ready Workforce
Improve the education, knowledge, skills, and health of residents to work and succeed in Appalachia. - Goal 3: Critical Infrastructure
Invest in critical infrastructure – especially broadband; transportation, including the Appalachian Development Highway System; and water/wastewater systems. - Goal 4: Natural and Cultural Assets
Strengthen Appalachia’s community and economic development potential by leveraging the Region’s natural and cultural heritage assets. - Goal 5: Leadership and Community Capacity
Build the capacity and skills of current and next-generation leaders and organizations to innovate, collaborate, and advance community and economic development.
Appalachian New York
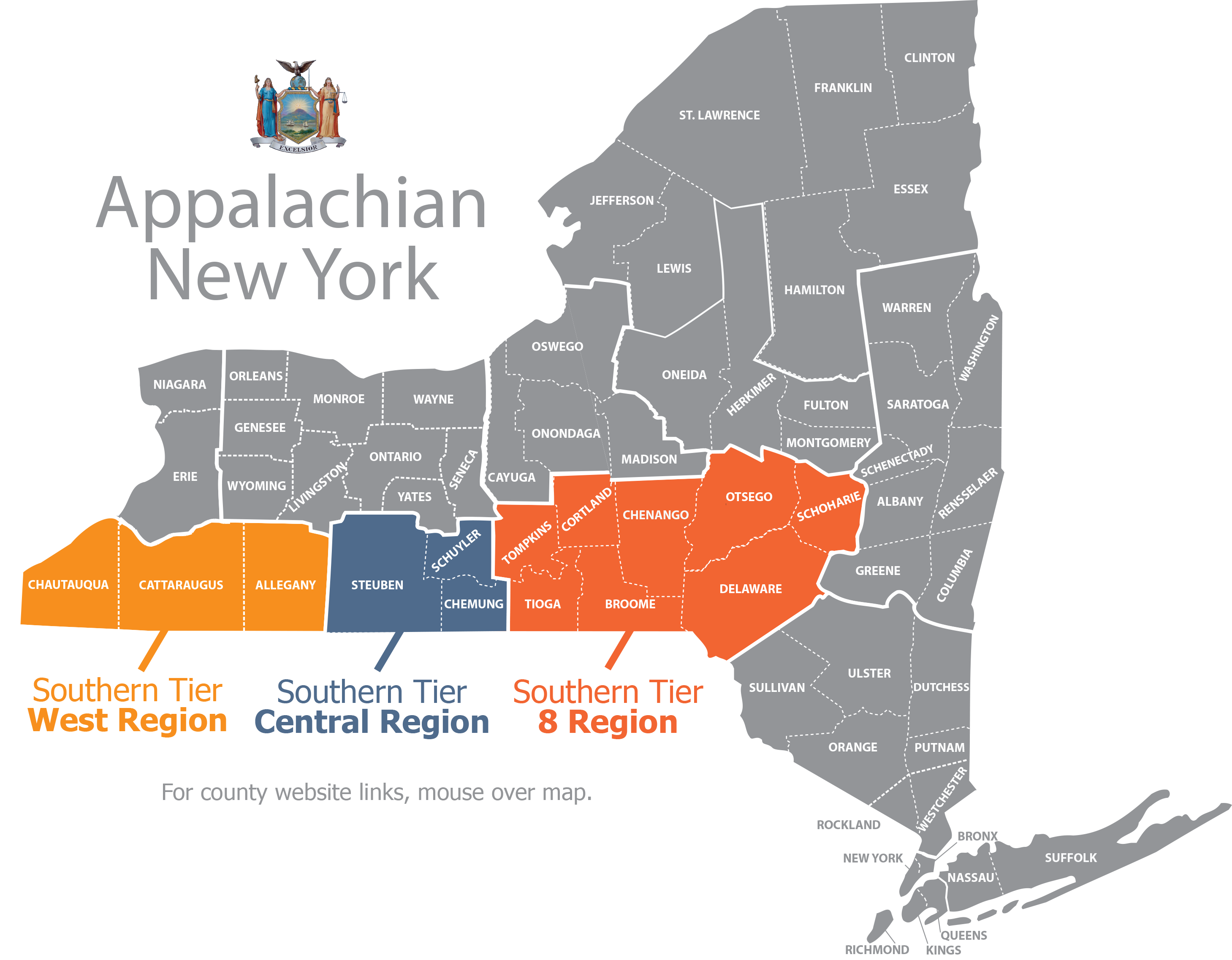
The Appalachian portion of New York State ("Appalachian New York"), contains the following fourteen counties: Allegany, Broome, Cattaraugus, Chautauqua, Chemung, Chenango, Cortland, Delaware, Otsego, Schoharie, Schuyler, Steuben, Tioga and Tompkins. This region is most commonly known as New York's "Southern Tier."
New York Policy and Program Development
The ARC Federal Fiscal Year grant solicitation cycle begins in April every year and extends for two months into June. Area Development Program grant awards provide matching funds for projects in or affecting New York’s fourteen Appalachian counties. New York State has established 27 strategies to meet the ARC’s first three general goals. These strategies provide the key State policy framework for ARC-grant funded projects in Appalachian New York.
Projects and Project Eligibility
Historically NYS’s ARC Program has supported projects in the following categories: Education and Job Training; Community Development; Leadership and Civic Capacity Building; Healthcare Access; Business Development; Research and Technical Assistance; Transportation; and Environment and Natural Resources.
All project proposals must implement at least one of the State strategies. In Allegany County, which the ARC has designated “At Risk,” financial assistance from ARC may not exceed 70% of the total eligible project cost. For projects in or affecting the other thirteen Appalachian counties, ARC funding may not exceed 50% of the total eligible project cost. There is a limit of $150,000 on the ARC-funded portion of all projects.
Local Development Districts
The first point of contact for potential sponsors of ARC Grant funded projects is the Local Development District (LDD) that serves the project’s proposed service area. The LDD’s provide technical assistance to potential sponsors with application preparation, prepare area wide plans to guide annual investment of ARC resources, and submit applications to the Department of State for consideration and inclusion in the annual Investment Package. The LDD’s and the respective counties they serve are:
Southern Tier 8 Regional Planning and Development Board
Southern Tier Central Regional Planning Board
Southern Tier West Regional Planning and Development Board
Program Partners
The Department of State is assisted by other State and Federal agencies in its administration of the Appalachian Program in New York State. The partner agencies provide technical assistance, project monitoring, research and data analysis and other assistance as needed. Certain agencies act as Basic Agency for those construction projects not directly administered by the Commission. The basic agencies review and approve the scope of work and cost breakdown prior to ARC approval.
State Program Partners
- NYS Department of State
- Local Government Efficiency
- Land Use Training and Technical Assistance
- Local Waterfront Revitalization
- Brownfield Opportunities Area
- NYS Department of Education
- NYS Department of Health
- NYS Department of Transportation
- NYS Empire State Development
- NYS Environmental Facilities Corporation
- Office of Community Renewal
- NYS Department of Environmental Conservation
- NYS Department of Labor
- NYS Energy and Research Development Authority
- NYS Office for Telecommunications (OFT)
Federal Program Partners
